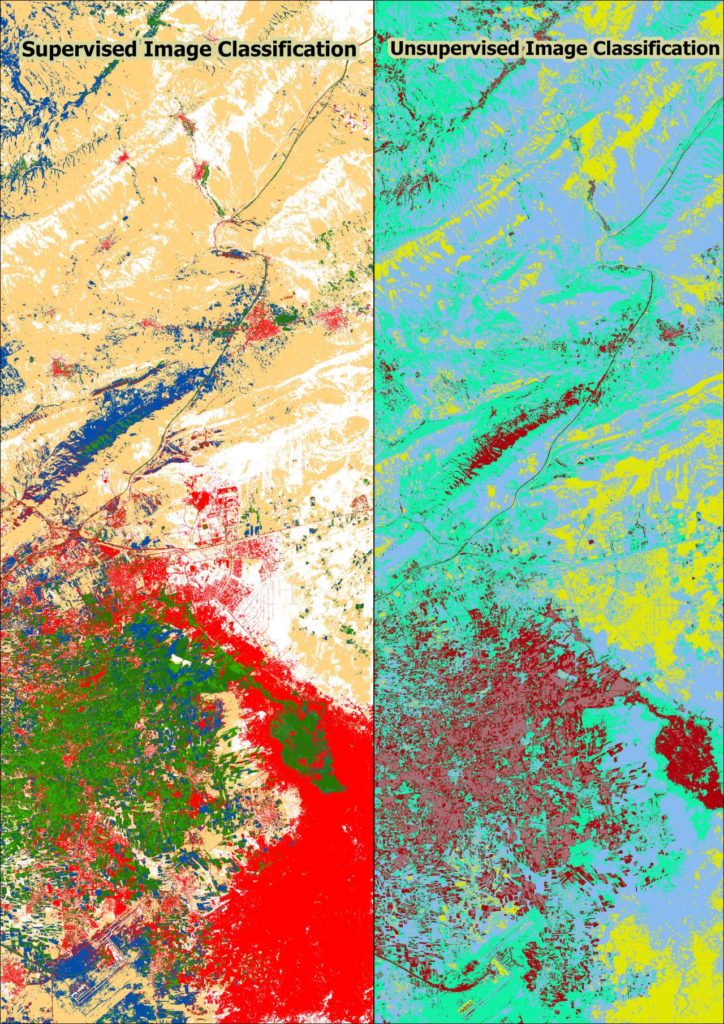
Supervised and unsupervised classification are two common methods used in GIS for analyzing and categorizing spatial data. Here’s a breakdown of the differences between the two :
Supervised Classification:
- Definition: Supervised classification is a method where the analyst provides a set of labeled training samples to the classification algorithm. These training samples consist of known or representative locations with predefined classes or categories.
- Process: The classification algorithm learns the patterns and characteristics of the training samples to create a classification model. This model is then applied to classify the remaining unlabeled data.
- Input: Supervised classification requires labeled training data where each sample is associated with a specific class or category.
- Output: The output of supervised classification is a thematic map or raster layer where each pixel or location is assigned to a specific class or category based on the learned model.
- Accuracy assessment: Since the training samples are labeled, it is possible to assess the accuracy of the classification by comparing the classified results with the known classes from the training data.
Unsupervised Classification:
- Definition: Unsupervised classification is a method where the classification algorithm automatically identifies patterns and structures in the data without any prior knowledge of the classes or categories.
- Process: The algorithm analyzes the statistical properties and spatial relationships of the data to group similar pixels or locations into clusters. These clusters are then assigned labels based on subsequent analysis by the analyst.
- Input: Unsupervised classification only requires the input data without any prior labeled samples.
- Output: The output of unsupervised classification is also a thematic map or raster layer, but the classes or categories are determined solely based on the inherent patterns in the data.
- Interpretation: Interpreting the resulting classes in unsupervised classification is usually more challenging since there is no predetermined knowledge about the classes. The analyst needs to analyze and assign meaningful labels to the identified clusters based on domain knowledge or further analysis.
Author of the text : Douha AKKARI, GIS Specialist, Geographer. Reach out her Linkedin Page.